Iso 2768 Hole Tolerance Chart M4
Metric thread size and tolerance calculator was developed to calculate major, minor and pitch diameters of the external (bolt) and internal (nut) metric threads according to ISO 724:1993 standard. In addition to basic size calculations of metric threads, tolerance calculations of different tolerance classes can be done according to ISO 965-1:1998 and ISO 965-2:1998 standards. There are two calculation options available, general engineering use or custom use. In general engineering use, calculations can be done by selecting a standard metric thread size from the list which contains metric thread sizes in the diameter range from 1.6 mm (M1.6) to 64 mm (M64). Tolerance class can be selected among the alternatives 6e, 6f, 6g and 4h for bolts and 5H, 6H, 7H and 6G for nuts. 6g and 6H are default values and selected class for commercial external threads and internal threads in ISO 965-1:1998. The user shall use 6g for bolts and 6H for nuts unless there is a specific requirement to use other tolerance classes.
Kumpulan Gambar Animasi Power Point Bergerak untuk PPT Keren Kalian! Berikut ini berbagai macam gambar animasi power point bergerak yang dapat kalian download atau “save as” dengan mudah. Gambar Animasi Bergerak Powerpoint Pembukaan. Kumpulan animasi bergerac powerpoint pembukaan kota 2017. Animasi bergerak powerpoint welcome - Pembukaan Selamat Datang at 20.02 Alangkah baiknya kita melakukan sapaan terlebih dahulu kepada audience kita dengan sopan dengan mengatakan selamat datang Atau Welcome di acara Persentase kami.
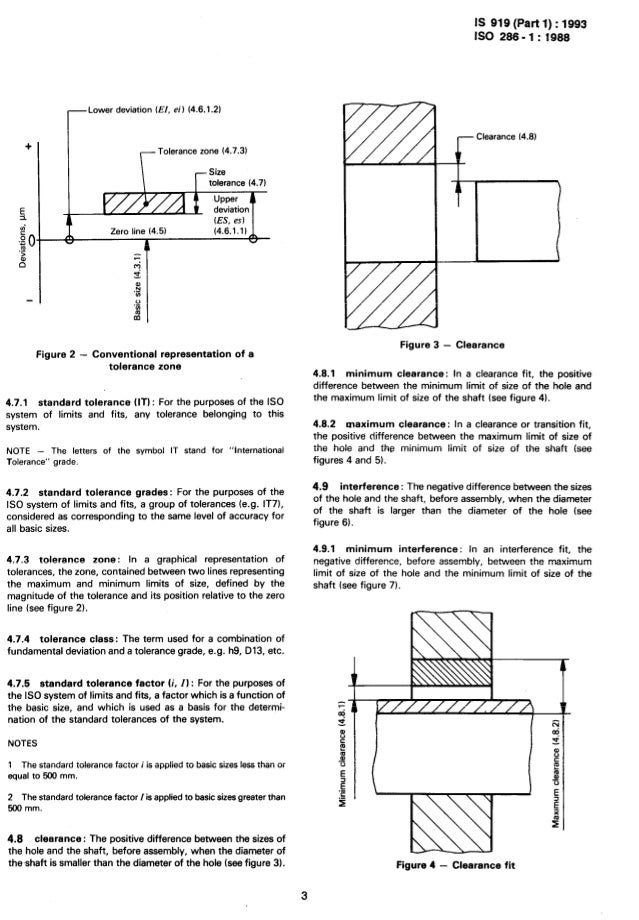
ISO Hole Tolerances (ISO 286-2) (3mm-400mm): ISO Hole Tolerances for chart given below shows range between 3mm to 400mm. Nominal Dimension and Tolerance Zone for Holes are in mm (Metric). ISO Hole Tolerances help the manufacturer to machine the parts with specified litims given by engineer.
In custom use, thread size, pitch and tolerance classes can be independently selected for custom engineering calculations. Some important notes from ISO metric screw threads standards: - External Screw Thread Designation: Nominal Diameter x Pitch - Tolerance class for pitch diameter - Tolerance class for major diameter (M10 x 1 5g 6g) - Internal Screw Thread Designation: – Nominal Diameter x Pitch - Tolerance class for pitch diameter - Tolerance class for minor diameter (M10 x 1 5H 6H) - If the two class designations for the pitch diameter and crest diameter are the same it is not necessary to repeat the symbols. (M10 x 1 6g) - According to ISO 1:2002, standard reference temperature for geometrical product specification is 20 °C. - Gauges and gauging for ISO general purpose metric threads are defined in the ISO 1502:1996 standard.
- The basic profile of ISO general purpose metric screw threads is defined in the ISO 68-1:1998 and given in the first figure below. External (bolt) thread root profile is given the 'Definitions' section. The list of metric screw thread used in general engineering applications are given in the.
Note: For more information on Metric screw threads including thread form, definitions, limits and fits for threads, standard series and combinations, thread designation, basic dimensions, dimensional effect of coating, formulas and details of MJ profile, please refer to pages 1930 - 19067 of. ISO metric screw thread basic profile according to ISO 68-1. Metric ISO Thread Calculator: INPUT PARAMETERS Calculation Type GENERAL ENGINEERING USE Metric Thread External Thread (Bolt) Tolerance Class * Internal Thread (Nut) Tolerance Class** CUSTOM USE Nominal Diameter Pitch Bolt Tolerance Class Tolerance Grades Deviations Pitch Diameter Tolerance Major Diameter Tolerance Nut Tolerance Class Tolerance Grades Deviations Pitch Diameter Tolerance Minor Diameter Tolerance Note: * 6g is normally selected for commercial external (bolt) threads. Use this tolerance class for commercial external (bolt) threads. For usage of the other classes, refer to ISO 965-1:1998. Note: ** 6H is normally selected for commercial internal (nut) threads.
Use this tolerance class for commercial internal threads. For usage of the other classes, refer to ISO 965-1:1998.
ISO Symbol Description Hole Basis Shaft Basis Clearance Fits H11/c11 C11/h11 Loose running fit for wide commercial tolerances or allowances on external members. H9/d9 D9/h9 Free running fit not for use where accuracy is essential, but good for large temperature variations, high running speeds, or heavy journal pressures. H8/f7 F8/h7 Close running fit for running on accurate machines and for accurate location at moderate speeds and journal pressures. H7/g6 G7/h6 Sliding fit not intended to run freely, but to move and turn freely and locate accurately. H7/h6 H7/h6 Locational clearance fit provides snug fit for locating stationary parts; but can be freely assembled and disassembled. Transition Fits H7/k6 K7/h6 Locational transition fit for accurate location, a compromise between clearance and interference.
H7/n6 N7/h6 Locational transition fit for more accurate location where greater interference is permissible. Interference Fits H7/p6 P7/h6 Locational interference fit for parts requiring rigidity and alignment with prime accuracy of location but without special bore pressure requirements. H7/s6 S7/h6 Medium drive fit for ordinary steel parts or shrink fits on light sections, the tightest fit usable with cast iron. H7/u6 U7/h6 Force fit suitable for parts which can be highly stressed or for shrink fits where the heavy pressing forces required are impractical. Preferred fits table (ANSI B4.2-1978) Basic Hole Tolerance classes for shafts Clearance Fits Transition Fits Interference Fits H6 g5 h5 js5 k5 m5 n5 p5 H7 f6 g6 h6 js6 k6 m6 n6 p6 r6 s6 t6 u6 x6 H8 e7 f7 h7 js7 k7 m7 s7 u7 d8 e8 f8 h8 H9 d8 e8 f8 h8 H10 b9 c9 d9 e9 h9 H11 b11 c11 d10 h10 Preferable fits of the hole-basis system (ISO 286-1:2010). Basic Shaft Tolerance classes for holes Clearance Fits Transition Fits Interference Fits h5 G6 H6 JS6 K6 M6 N6 P6 h6 F7 G7 H7 JS7 K7 M7 N7 P7 R7 S7 T7 U7 X7 h7 E8 F8 H8 h8 D9 E9 F9 H9 h9 E8 F8 H8 D9 E9 F9 H9 B11 C10 D10 H10 Preferable fits of the shaft-basis system (ISO 286-1:2010) Note: For economic reasons, the first choice for a fit should, whenever possible, be made from the tolerance classes shown with green color.